1、水题
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define int long long
#define endl 'n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m;
int a[N];
void init(int n){
for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){
a[i] = 0;
}
}
int qc(int a, int b , int c){
return (a + b + c)/2;
}
int alg(int a , int b , int c){
int cc = qc(a , b , c);
return (cc * (cc - a) * (cc - b) * (cc - c));
}
void solve()
{
int a , b , c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
if(a + b <= c || a + c <= b || b + c <= a){
cout << -1;
}
else
cout << alg(a , b , c);
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
// cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
3、模拟题,找规律,第一行和最后一行只有两个数,其余行都是三个数。
第一行特殊处理,其余行: 就是当前所在行
,
就是所在行第s个数 , 每行第一个数是
, 因此所在列就是r – 1 + s。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
long long n , m;
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++){
long long x;
cin >> x;
if(x <= 1){
cout << 1 << " " << x + 1 << endl;
}
else{
long long r = (x + 1) / 3 + 1;
long long st = x - ((r - 1) * 3 - 1);
long long dc = r - 1 + st;
cout << r << " " << dc << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}4、![]() 考虑找到
考虑找到的所有可能取值,取值上界应该为
。由于
,因此每个肯定不超过64种取值。用三重循环找到所有
的所有取值,复杂度为
。注意
判断可能会爆long long , 所以在判断是否到达上界需要用
。用数组或者set去存每种取值,然后从小到大排序。按照题目条件对每个询问搜索即可(二分/暴力)。整体复杂度
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl 'n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f;
const LL llinf = 2e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m;
LL a , b , c;
set<LL>st;
void solve()
{
cin >> a >> b >> c;
vector<LL>aa , bb , cc;
aa.pb(1);
bb.pb(1);
cc.pb(1);
LL x = 1;
while(a != 1 && x < llinf / a){
x *= a;
aa.pb(x);
}
LL y = 1;
while(b != 1 && y < llinf / b){
y *= b;
bb.pb(y);
}
LL z = 1;
while(c != 1 && z < llinf / c){
z *= c;
cc.pb(z);
}
for(int i = 0 ; i < aa.size() ; i ++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < bb.size() ; j ++){
for(int z = 0 ; z < cc.size() ; z ++){
st.insert(aa[i] + bb[j] + cc[z]);
}
}
}
int m;
cin >> m;
for(int i = 0 ; i < m ; i ++){
LL que;
cin >> que;
auto it = st.upper_bound(que);
while(*it - que == 1){
que = *it;
it = st.upper_bound(que);
}
cout << que + 1 << " " << (*it - que - 1) << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
// cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
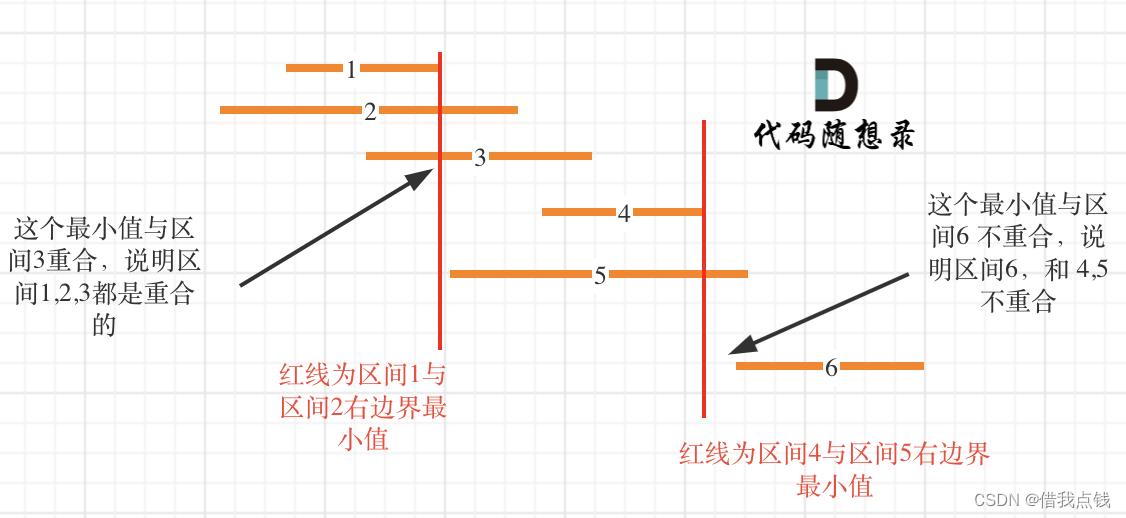
5、 方法很多,大体思路为将类型一样的宝石放到一起,将他们的作用区间进行合并,然后对整个数组进行区间修改。
区间合并:将所有区间按照左端点排序,遍历区间,若当前左端点与前一个区间右端点有重合部分,则将他们合并成一个区间,否则将前一个区间存下来,当前区间为一个新的区间。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl 'n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m;
int a[N];
void init(int n){
for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){
a[i] = 0;
}
}
struct BIT{//Binary indexed Tree(树状数组)
int n;
vector<int> tr;
BIT(int n) : n(n) , tr(n + 1 , 0){
}
int lowbit(int x){
return x & -x;
}
void modify(int x , int modify_number){
for(int i = x ; i <= n ; i += lowbit(i)){
tr[i] += modify_number;
}
}
void modify(int l , int r , int modify_number){
modify(l , modify_number);
modify(r + 1 , -modify_number);
}
int query(int x){
int res = 0;
for(int i = x ; i ; i -= lowbit(i))
res += tr[i];
return res;
}
int query(int x , int y){
return query(y) - query(x);
}
};
void solve()
{
int n , m , q;
cin >> n >> m >> q;
vector<int>len(m + 5);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i++){
cin >> len[i];
}
BIT bit(n);
vector<pair<int,int>>que;
for(int i = 0 ; i < q ; i ++){
int x , y;
cin >> x >> y;
que.pb({x , y});
}
sort(que.begin() , que.end());
int r = 0 , pos = 0;
for(int i = 0 ;i < q ; i ++){
if(que[i].x != pos){
pos = que[i].x;
r = 0;
}
bit.modify( max(r + 1, que[i].y) , min(que[i].y + len[pos] - 1 , n) , 1);
r = min(que[i].y + len[pos] - 1 , n);
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
cout << bit.query(i)<<" ";
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
// cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}6、删除区间求中位数比较困难。相反,增加数求区间中位数就是一道对顶堆的板子题了。因此考虑逆着做题,先将所有会飘走的气球放弃,将其余气球加入对顶堆。然后再从后往前依次添加气球,维护对顶堆找答案即可(对顶堆网上一大堆模板)。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define LL long long
#define pb push_back
#define x first
#define y second
#define endl 'n'
const LL maxn = 4e05+7;
const LL N = 5e05+10;
const LL mod = 1e09+7;
const int inf = 0x3f3f;
const LL llinf = 5e18;
typedef pair<int,int>pl;
priority_queue<LL , vector<LL>, greater<LL> >mi;//小根堆
priority_queue<LL> ma;//大根堆
LL gcd(LL a, LL b){
return b > 0 ? gcd(b , a % b) : a;
}
LL lcm(LL a , LL b){
return a / gcd(a , b) * b;
}
int n , m;
int a[N];
void init(int n){
for(int i = 0 ; i <= n ; i ++){
a[i] = 0;
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> n;
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i ++){
cin >> a[i];
}
cin >> m;
double ans[m + 5];
int que[m + 5];
int vis[n + 5];
memset(vis,0,sizeof vis);
for(int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i ++){
cin >> que[i];
vis[que[i]] = 1;
}
for(int i = 1 ;i <= n ; i ++){
if(!vis[i]){
ma.push(a[i]);
}
}
while(ma.size() > mi.size()){
mi.push(ma.top());
ma.pop();
}
for(int i = m ; i > 0 ; i --){
if((mi.size() + ma.size()) % 2 == 0){//偶数
int x = mi.top();
int y = ma.top();
ans[i] = (double)(1.0 * x + y) / 2;
}
else{
double x = mi.top();
ans[i] = (double)(1.0 * x);
}
int yy = mi.top();
if(a[que[i]] > yy){
mi.push(a[que[i]]);
}
else{
ma.push(a[que[i]]);
}
while(mi.size() > ma.size() + 1){
ma.push(mi.top());
mi.pop();
}
while(ma.size() > mi.size()){
mi.push(ma.top());
ma.pop();
}
}
for(int i = 1 ; i <= m ; i++){
printf("%.1f " , ans[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cout.precision(10);
int t=1;
// cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_61825750/article/details/134624528
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_21994.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!