文章目录
一、Vue简介
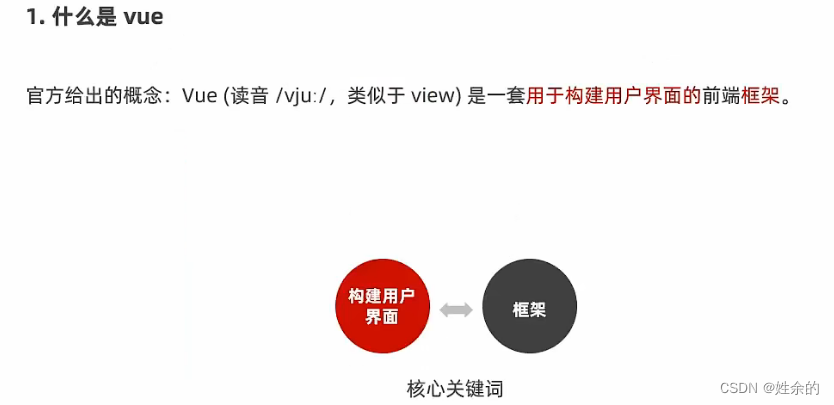
1、什么是Vue
1)构建用户界面
2)框架
- 框架时一套现场的解决方案,程序员智能遵守框架的规范,去编写自己的业务功能
- 要学习vue,就是在学习vue框架中规定的用法!
- vue指令、组件(是对UI结构的复用)、路由、Vuex、vue组件库
- 只有把上面罗列的内容掌握以后,才有开发vue项目的能力
2、Vue的两个特性
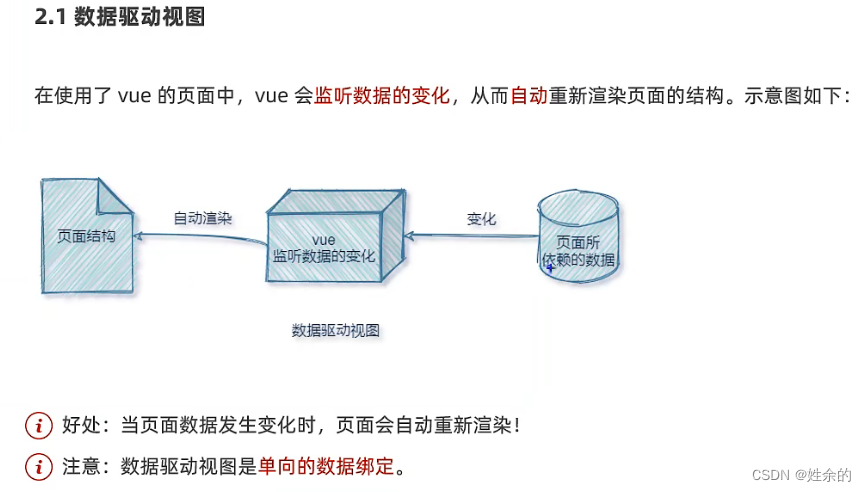
1)数据驱动视图
2)双向数据绑定
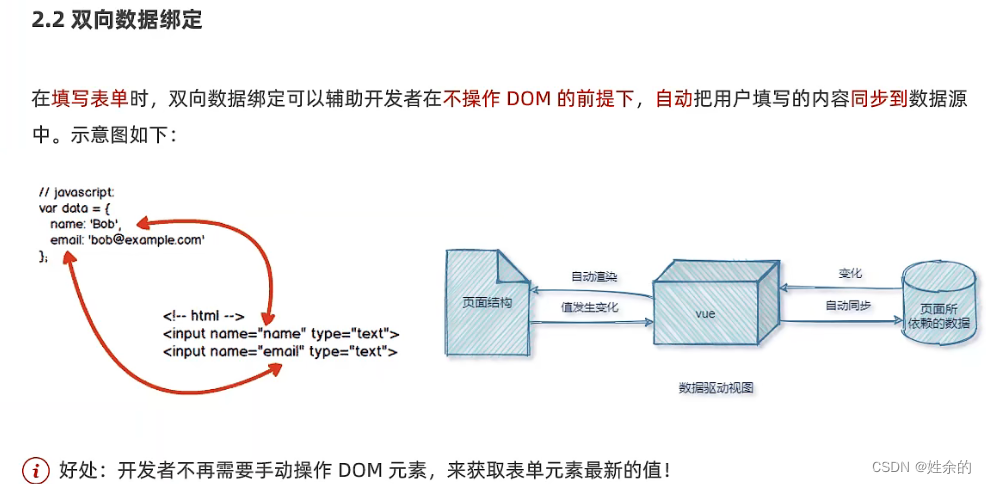
- 在网页中,
form表单负责采集数据,Ajax负责提交数据 - 好处:程序员不需要手动添加DOM操作即可得到表单最新值
- js数据的变化,会被自动渲染到页面上
- 页面上表单采集的数据发生变化的时候,会被vue自动获取到,并更新到js数据中
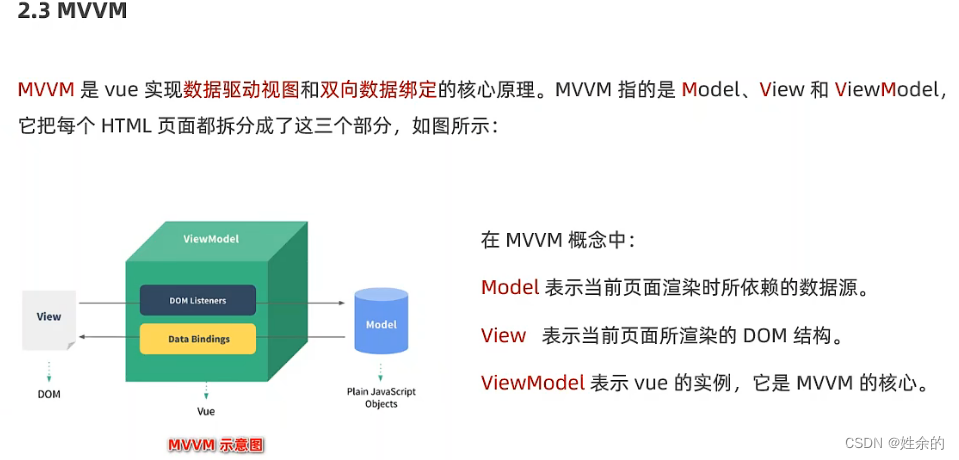
3)、MVVM
(1)、Model、View、ViewModel
Model:表示当前页面渲染是所依赖的数据源
View:表示当前页面所渲染的DOM结构
ViewModel:表示vue的实例,他是MVVM的核心
(2)、MVVM的工作原理
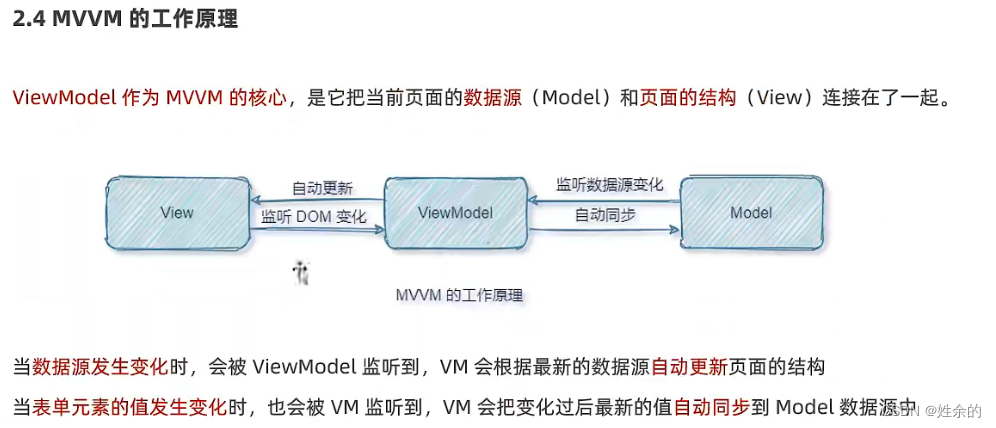
注意:数据驱动试图和双向数据绑定的底层原理是MVVM(Model数据源、View视图、ViewModel就是vue实例)
4、Vue的版本

二、Vue的使用
1、基本使用步骤

2、准备所需文件
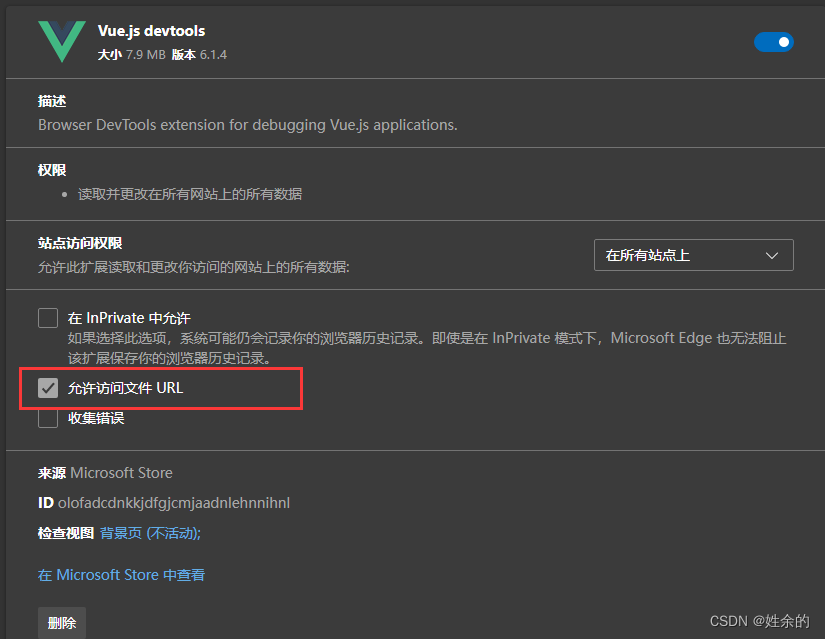
- 我们在Edge浏览器(google请自行找寻扩展包)下载
vue扩展(虽然现在不知道是干嘛用的)并且管理扩展里面点击详细信息让它能够访问文件的URL
- 在官网下载Vue.js,点击下面的下载就可以直接下载Vue.js
下载Vue.js
3、Vue第一个网页
使用Vue将数据渲染到页面上
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="" />
</head>
<body>
<!-- 希望vue能够控制下面这个div,帮我们把数据渲染到div内部-->
<div id="app">{{ username }}</div>
<!-- 1.导入Vue的库文件,在window全局就有了Vue这个构造函数-->
<script src="./lib/vue.js"></script>
<!-- 2.创建Vue的实例对象-->
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
//el属性是固定的写法,表示当前vm实例要控制页面上的哪个区域,接收的值是一个选择器
el: '#app',
//data对象就是要渲染到页面上的数据
data:{
username: '张三'
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
1)、基本代码与MVVM的对应关系

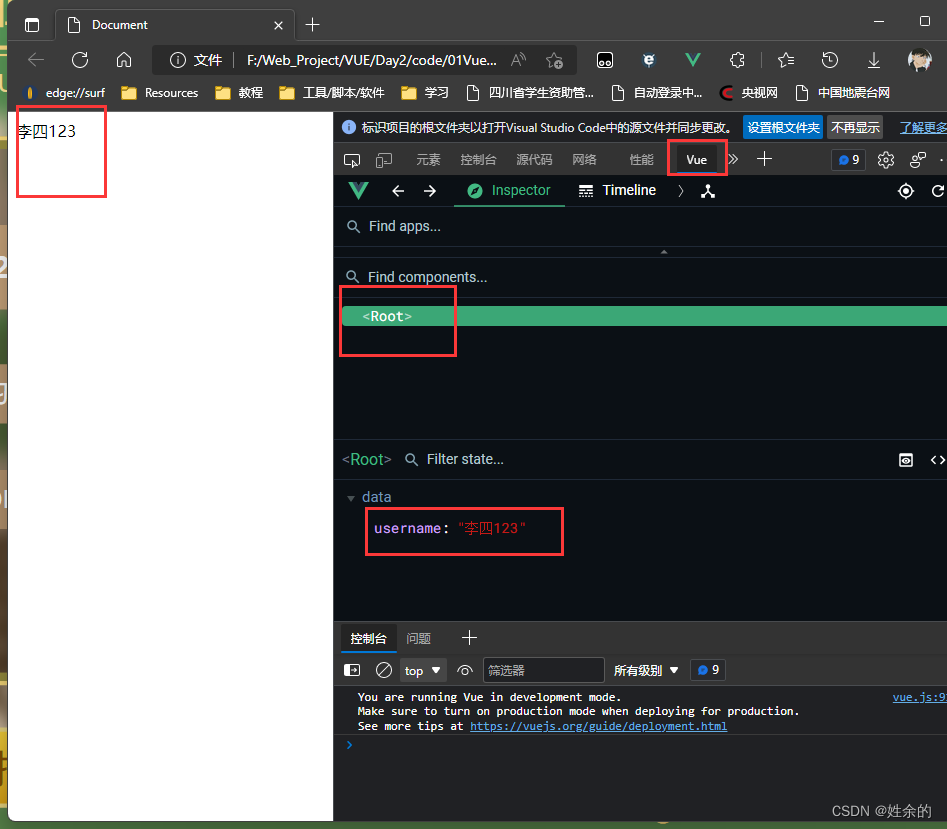
4、使用Edge浏览器中的vue-devtools
我们打开所写的页面,按F12 或者 右键-->检查,找到Vue如下图:就可以查看了
5、Vue的指令与过滤器
1)指令的概念

1.1)内容渲染指令
- v-text指令的缺点:会覆盖元素内部原有的内容
- {{ }} 插值表达式:在实际开发中用的最多,只是内容的占位符,不会覆盖原有内容
- v-html 指令的作用:可以把带有标签的字符串,渲染为真正标签的html内容
1.2)属性绑定指令v-bind
<div :title="'box' + index">这是一个div</div>
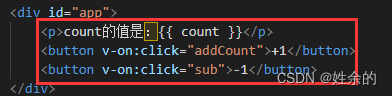
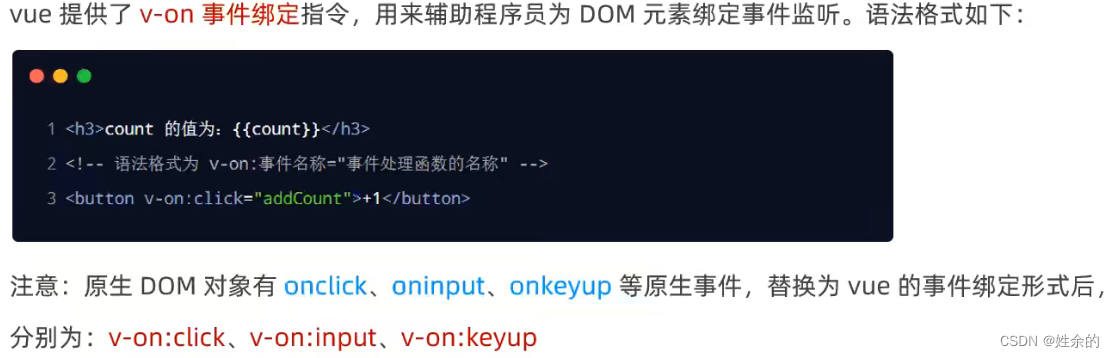
1.3)事件绑定指令v-on
我们将button进行事件绑定:
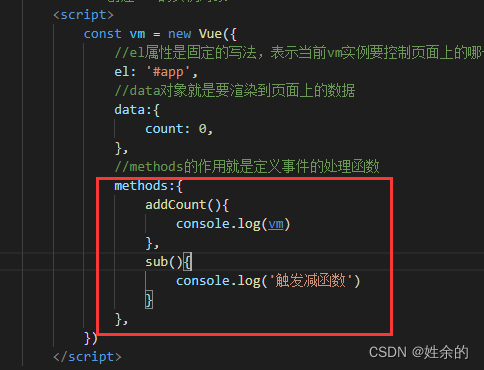
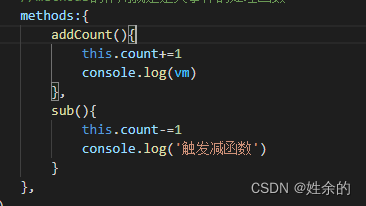
我们将所需要的函数写在与data同级的methods里
然后我们打印我们的vm实例,在浏览器中查看,点击+1按钮如图:
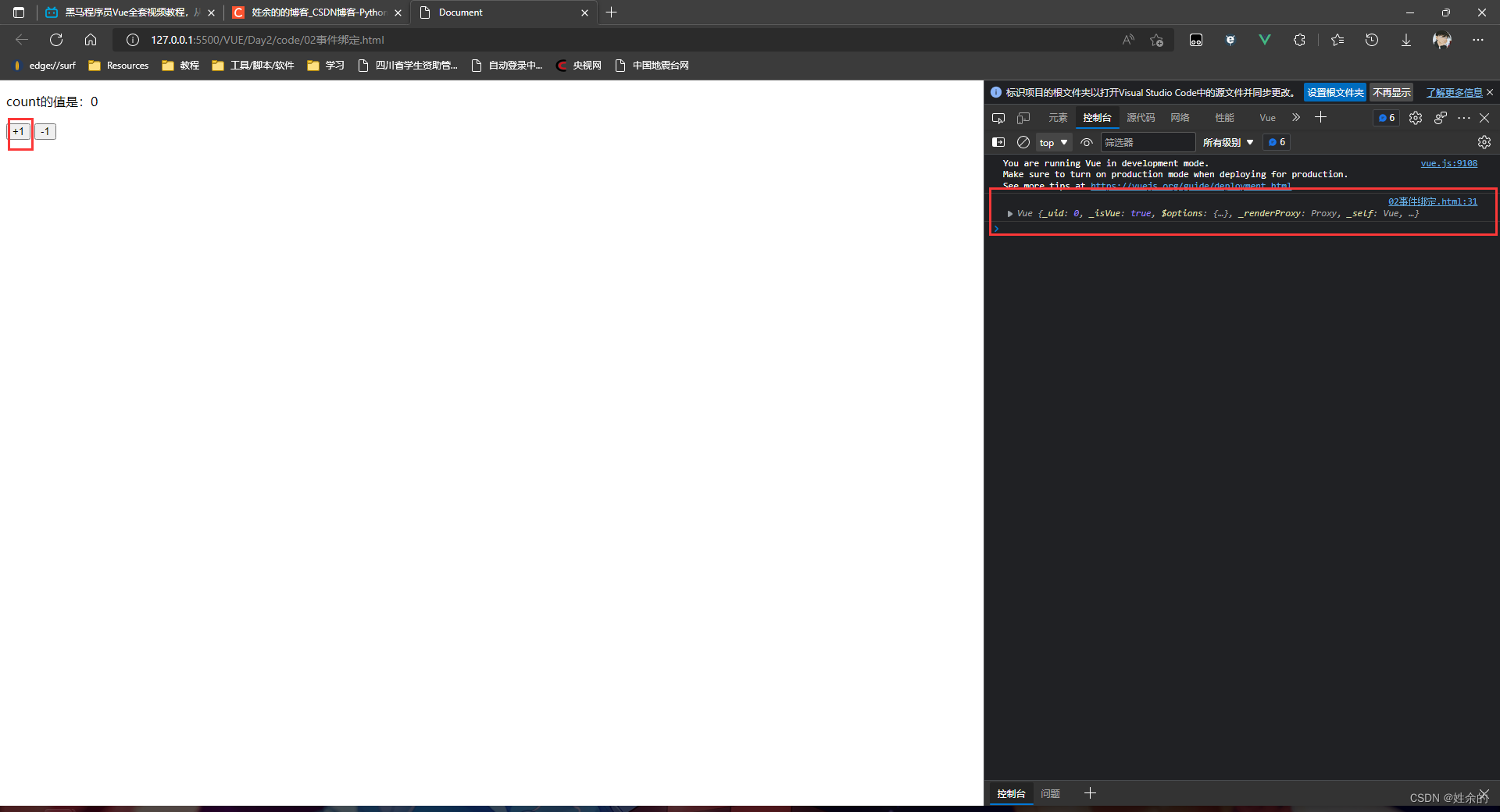
我们得到了一个返回的值,打开右边的对象,然后能看见一个count值:

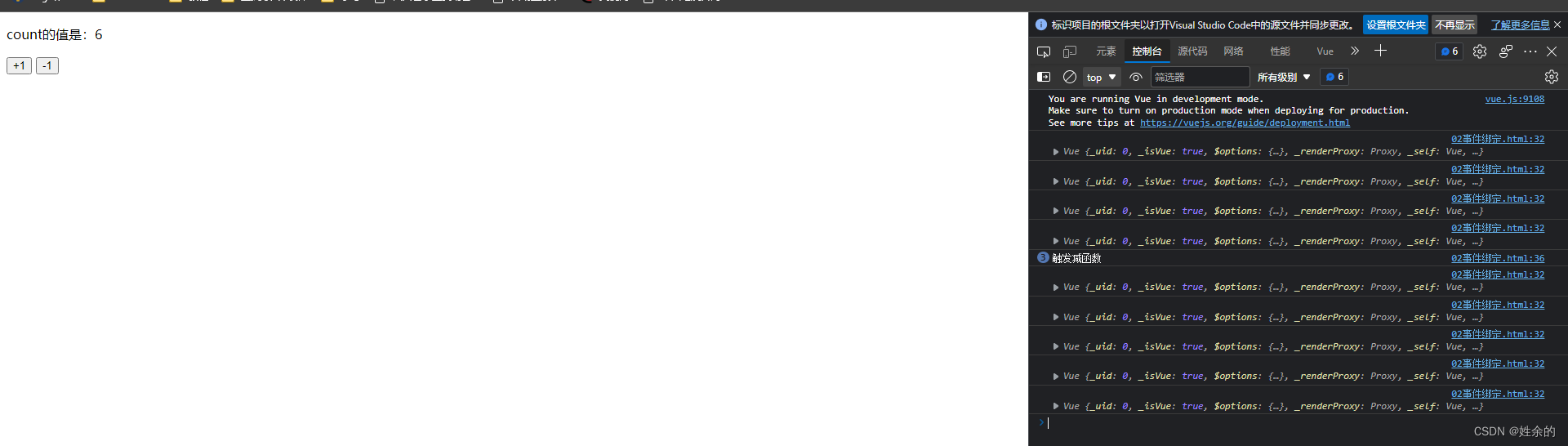
之后在代码内使用对象vm来调用,或者this(代表vm),vm.count或者this.count
这样就成功了
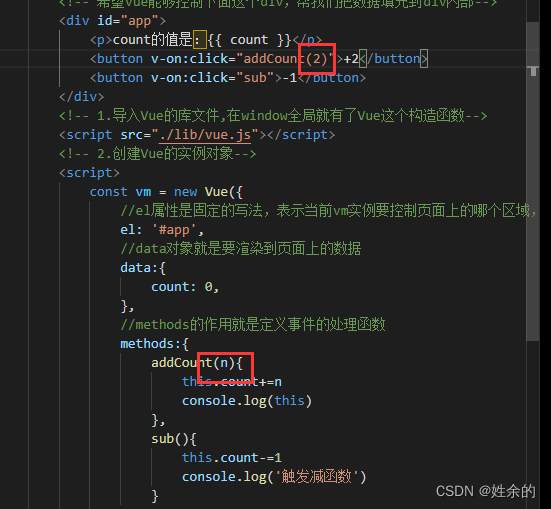
我们还能进行传参:
事件对象
当我们想实现count为偶数时为红色,count为奇数时为空。那么我们可以在add传入的参数里添加$event
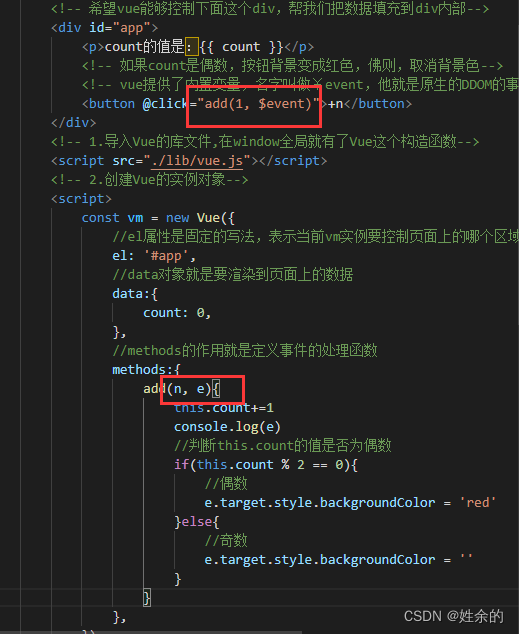
若我们没有传入数字也就是n,那么上面的@click就不需要任何参数,只需要在methods中添加一个e就可以了
这时我们在进入浏览器查看:
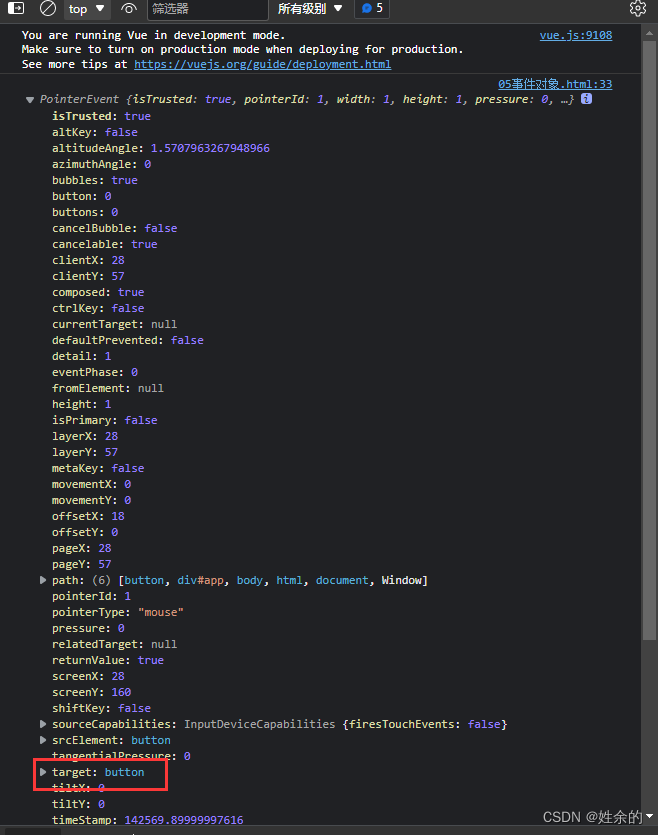
这时我们发现button在target下,所以我们使用e.target调用button,之后需要设置什么属性都可以直接展开逐一调用
v-on总结:
1.4)事件修饰符
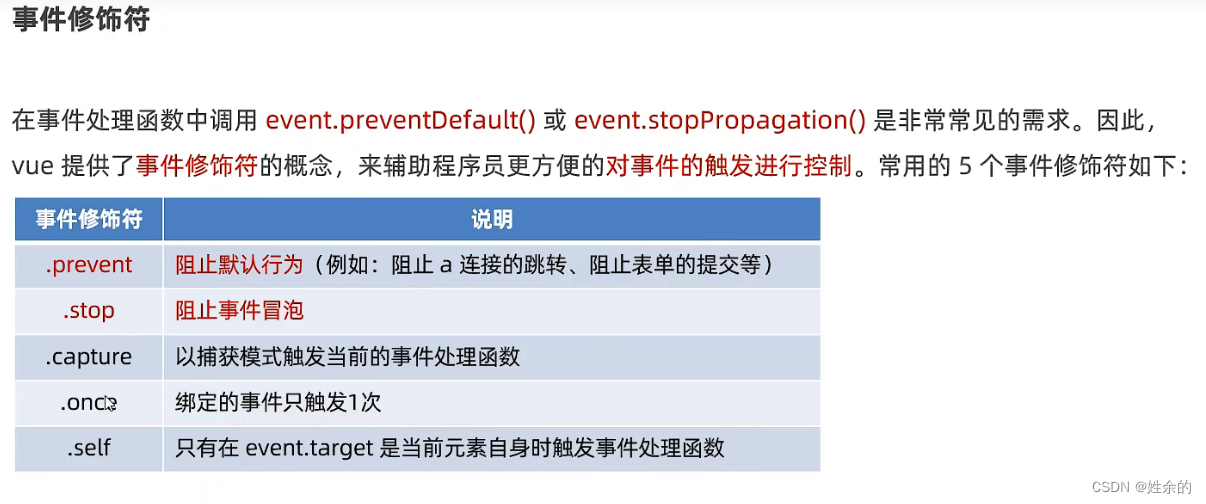
.stop
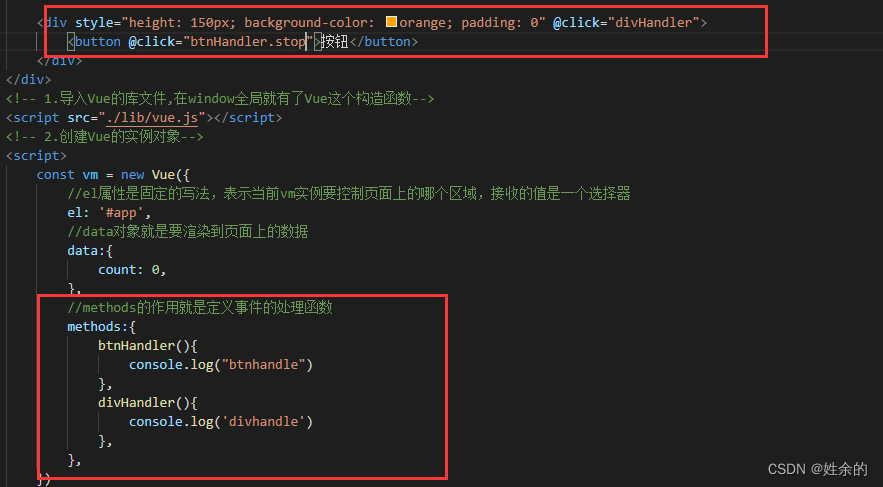
1.5)按键修饰符
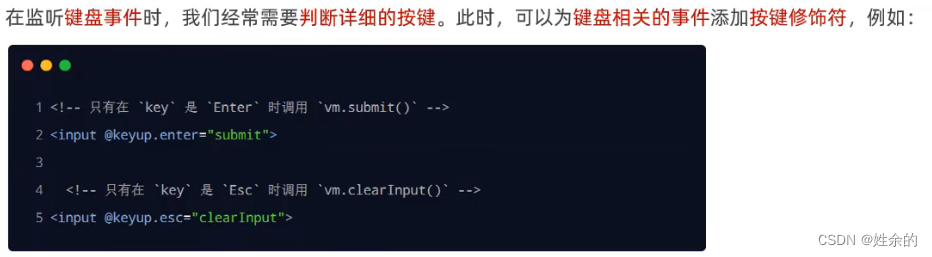
1.6)双向绑定指令v-model

可用:
v-model指令修饰符

1.7)条件渲染指令v-if
v-show的原理是动态为元素添加或一处 display:none样式来实现元素的显示和隐藏-
如果要频繁的切换元素的显示状态,用v-show性能会更好 v-if的原理是每次动态创建或移除元素,从而来实现元素的显示和隐藏-
如果刚进入页面的时候,某些元素不需要被展示,而且后期这个元素很可能也不需要被展示出来,此时v-if的性能会更好 - 在实际开发中,绝大多数情况,不用考虑性能问题,直接使用 v-if 就好了
v-if还可以单用:
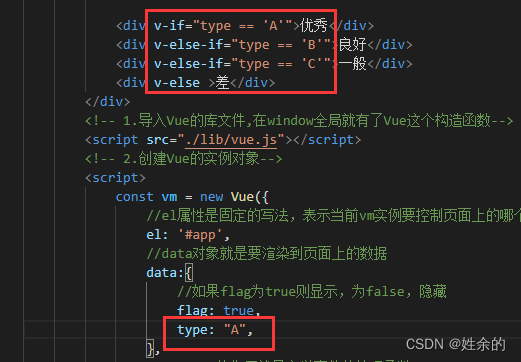
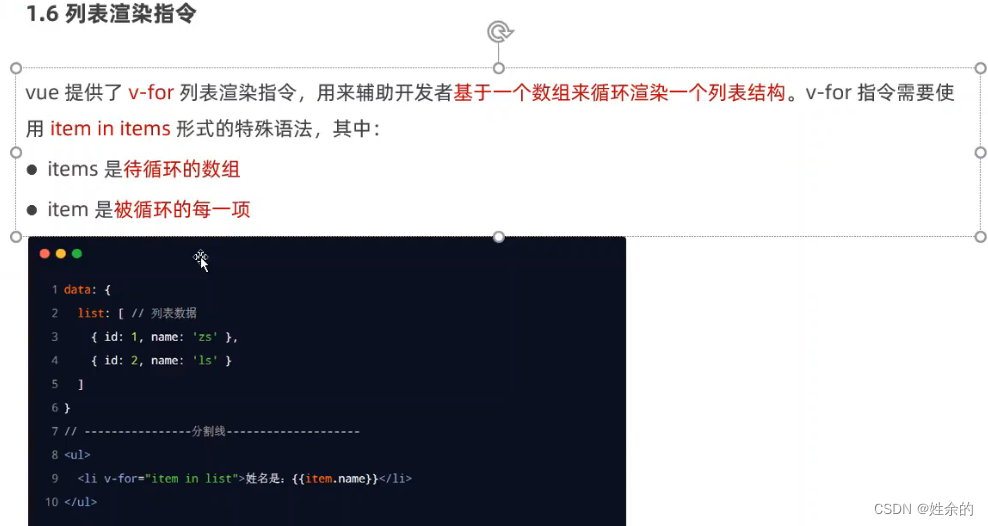
1.8)列表渲染指令v-for(2022.7.3)
1.8.1)key的注意事项
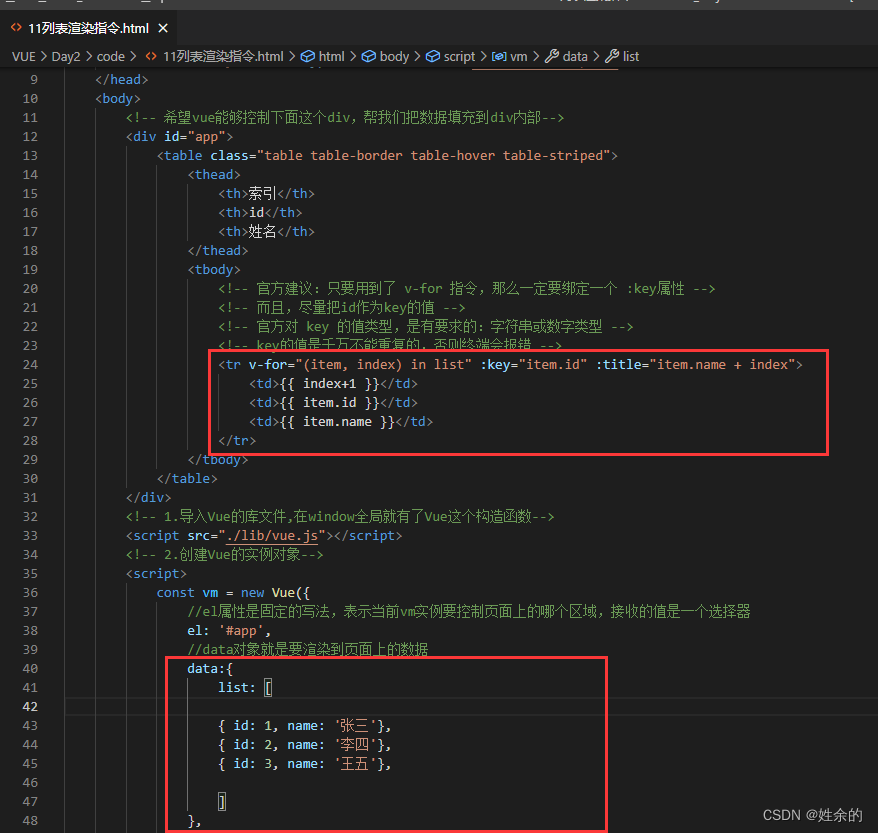
1.8.2)v-for案例(品牌列表案例)
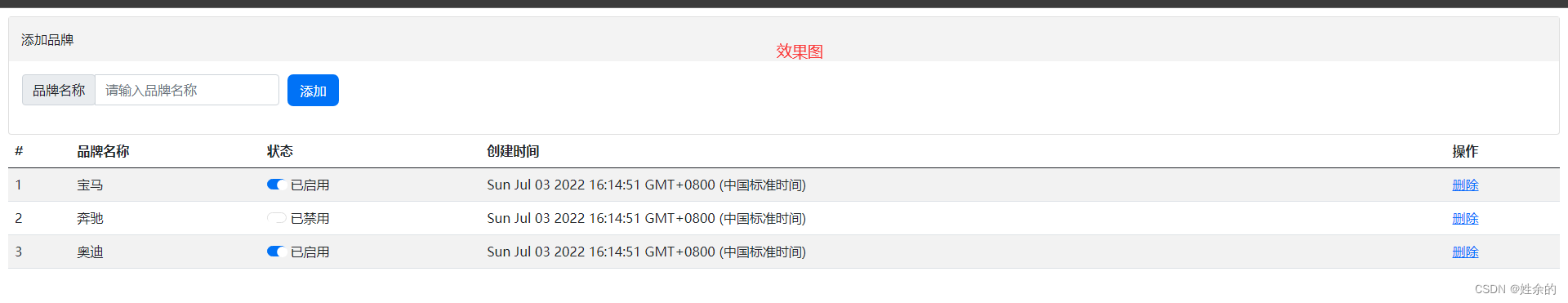
index.html(主页面,包含vue代码)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>品牌列表渲染</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./lib/bootstrap.css" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/index.css">
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<!-- 卡片区域-->
<div class="card">
<div class="card-heard">
添加品牌
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<!-- form表单元素有submit事件-->
<form @submit.prevent="add">
<div class="form-row align-item-center">
<div class="col-auto">
<div class="input-group mb-2">
<div class="input-group-prepend">
<div class="input-group-text">品牌名称</div>
</div>
<!-- 接收值得表单-->
<input type="text" class="form-control" placeholder="请输入品牌名称" v-model.trim="brand">
</div>
</div>
<!-- 添加按钮-->
<div class="button">
<button type="submit" class="btbm btm-primary mb-2">添加</button>
</div>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<!-- 表格区域-->
<table class="table table-border table-hover table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">#</th>
<th scope="col">品牌名称</th>
<th scope="col">状态</th>
<th scope="col">创建时间</th>
<th scope="col">操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="item in list" :key="item.id">
<td>{{ item.id }}</td>
<td>{{ item.name }}</td>
<td>
<div class="cunstom-control cunstom-switch">
<!-- lable 设置滑动checkbox-->
<label class="huadong">
<!-- checkbox-->
<input type="checkbox" style="display: none;" class="custom-control-input" :id="'cunstomSwich'+item.id" v-model="item.status">
<!-- 滑动的圆圈-->
<div class="check"></div>
<!-- 底色-->
<div class="circle"></div>
</label>
<!-- 设置是否禁用-->
<label class="custon-control-label" :for="'cunstomSwich'+item.id" v-if="item.status == true">已启用</label>
<label class="custon-control-label" :for="'cunstomSwich'+item.id" v-else>已禁用</label>
</div>
</td>
<td>{{ item.time }}</td>
<td>
<a href="javascript:;" @click="remove(item.id)">删除</a>
</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
<script src="./lib/vue.js"></script>
<!-- 2.创建Vue的实例对象-->
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
//el属性是固定的写法,表示当前vm实例要控制页面上的哪个区域,接收的值是一个选择器
el: '#app',
//data对象就是要渲染到页面上的数据
data:{
//用户输入的品牌名称
brand: '',
//下一个可用的id
nextid: 4,
//品牌数据列表
list: [
{ id: 1, name: "宝马",status: true, time: new Date() },
{ id: 2, name: "奔驰",status: false, time: new Date() },
{ id: 3, name: "奥迪",status: true, time: new Date() },
]
},
//methods的作用就是定义事件的处理函数
methods:{
remove(id){
this.list = this.list.filter(item => item.id !== id)
},
//阻止表单的默认提交行文之后,触发add方法
add(){
//若果判断到brand的值为空字符,则return出去
if(this.brand == ''){ return alert('必须填写品牌名称')}
//如果没有被return出去,应该执行添加逻辑
//1、先把要添加的品牌对象,整理出来
//往this.list数组中push步骤 1 中的对象
//3、清空 this.brand ;让 this.nextid 自增 +1
const obj = {
id : this.nextid,
name: this.brand,
status: true,
time: new Date(),
}
this.list.push(obj)
this.brand = ''
this.nextid++
},
},
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
index.css(设置位置和滑动checkbox)
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
border: none;
}
#app{
margin-top: 10px;
margin-left: 10px;
border-radius: 3px;
margin-right: 10px;
}
.card{
height: 145px;
width: 1900px;
}
.card-heard{
background-color: #f3f3f3f3;
padding-top: 15px;
padding-left: 15px;
padding-bottom: 15px;
}
.col-auto {
width: 315px;
height: 39px;
float: left;
}
.button{
height: 39px;
width: 63px;
float: left;
margin-left: 10px;
}
.btbm{
height: 39px;
width: 63px;
background-color: #0072F6;
color: #fff;
border-radius: 7px;
text-align: center;
}
.huadong{
position: relative;
z-index: 1;
}
.check{
width: 1.5rem;
height: .8rem;
border-radius: 100rem;
border: 1px solid #dddddd;
transition: .3s;
}
.circle{
width: .8rem;
height: .8rem;
border-radius: 50%;
background: #fff;
position: absolute;
left: 1px;
top: 1px;
transform: translateX(0rem);
transition: .3s;
}
input:checked ~.check{
background: #0072F6;
transition: .3s;
border-color: #0072F6;
}
input:checked ~ .circle{
transform: translateX(.7rem);
transition: .3s;
}
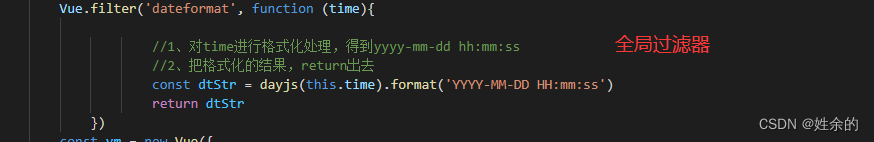
2)、过滤器

- 偷一下懒
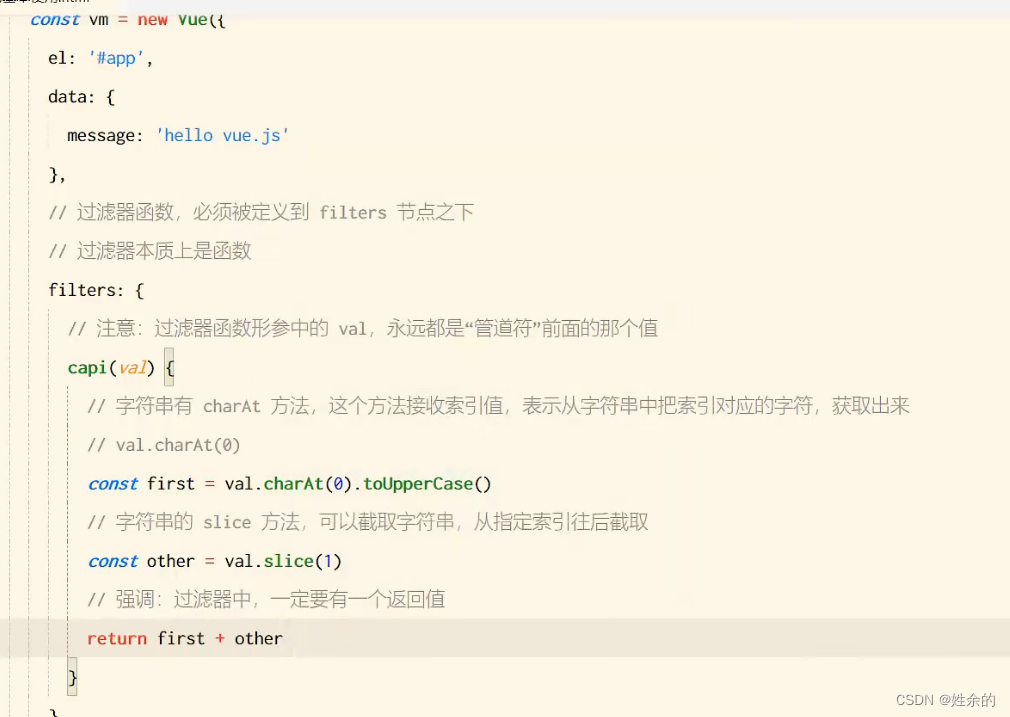
2.1)、全局过滤器

2.2)、过滤器的兼容性

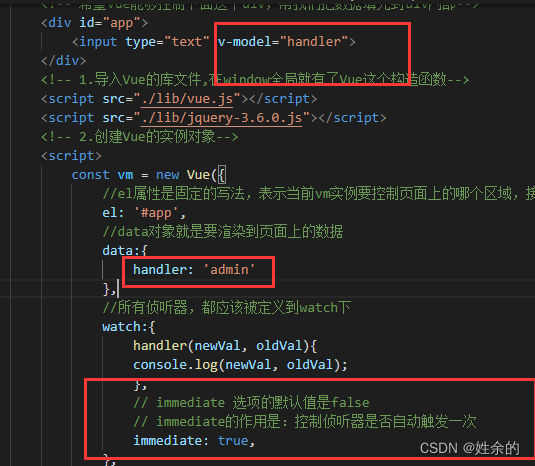
6、侦听器
1)、什么是侦听器

2)、侦听器的基本语法
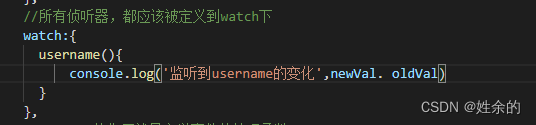
3)、侦听器的格式
3.1)、方法格式的侦听器
3.2)、对象格式的侦听器
3.2.1)、深度侦听
- 深度侦听对象
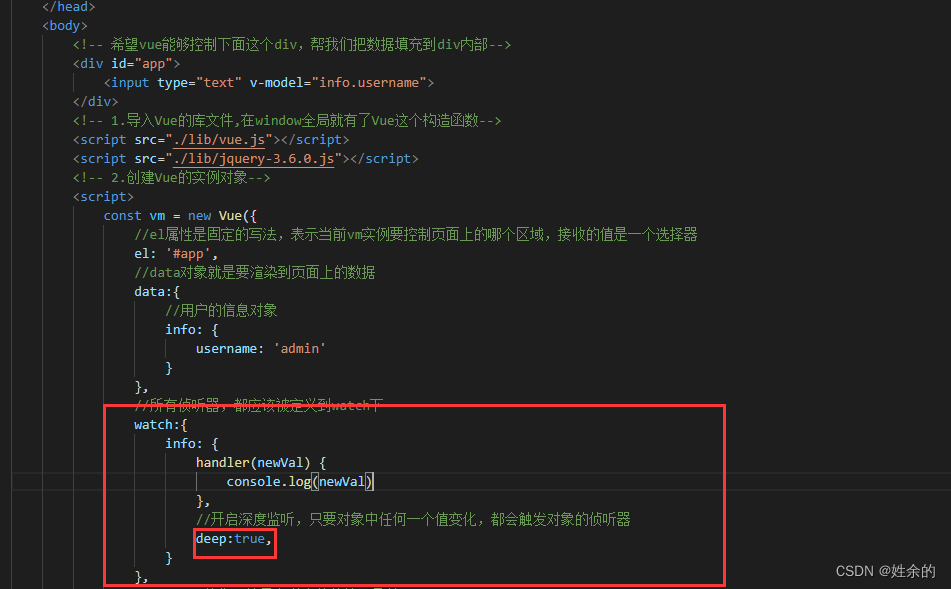
- 深度侦听对象属性
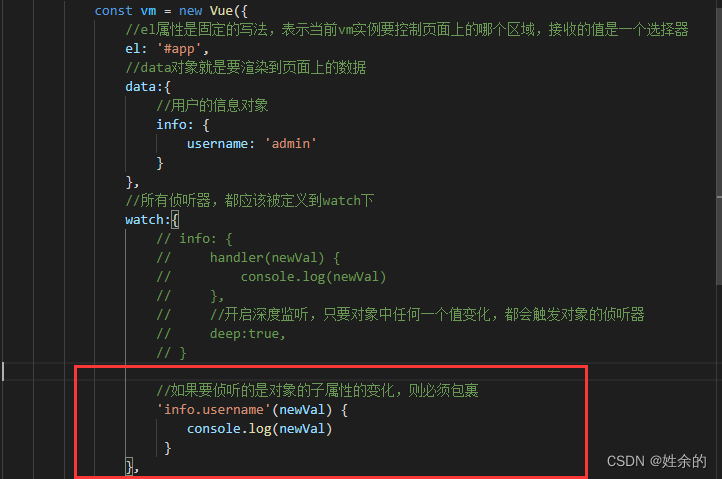
7、计算属性
1)、特点:
1、顶i的时候,要被定义为“方法“
2、在使用计算属性的时候,当普通的属性使用即可
2)、好处:
1、实现了代码的复用
2、只要计算属性中依赖的数据源变化了,则计算属性会自动重新求值
例子:
1)、什么是计算属性

8、axios
1)、axios的基本语法

2)、axios的基本使用
2.1)、发起GET请求
<script>
//1、调用axios方法得到的返回值是Promise对象
const result = axios({
//请求方式
method: 'GET',
//请求的地址
URL: 'localhost:3306',
//URL中的查询参数
params: {
id: 1,
},
//请求体参数
data: {}
}).then(function(result){
console.log(result)
})
</script>
2.2)、发起POST请求
<script>
document.querySelector("#btnPost").addEventListener('click', async function(){
//如果调用某方法的返回值是Promise实例,则前面可以添加await!
//await 只能用在被 async”修饰“的方法中
//1、调用axios之后,使用async/await进行简化
//2、使用解构赋值,从axios封装的大对象中,把data属性解结出来
//3、把解结出来的data属性,使用 冒号 进行重命名,一般都重命名为{ data : res }
const { data : res} = await axios({
method: "POST",
url: "http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/post",
})
console.log(res.data);
})
</script>
2.3)、POST、GET原生
<script>
document.querySelector("#btnGET").addEventListener('click', async function(){
/* axios.get('url'地址,{
//GET 参数
params: {}
})
*/
const { data : res} = await axios.get('http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/getbooks', {
params: {id:1}
})
console.log(res);
})
document.querySelector("#btnPOST").addEventListener('click', async function(){
/* axios.post('url'地址,{
post请求体数据
})
*/
const { data : res} =
await axios.post('http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/post',
{
name:'zs', gender:'女'
})
console.log(res);
})
</script>
9、总结
1)、了解vue的基本使用步骤

2)、掌握vue中常见指令的基本用法

3)、了解过滤器(Vue3已删除)
3.1)、过滤器注意事项
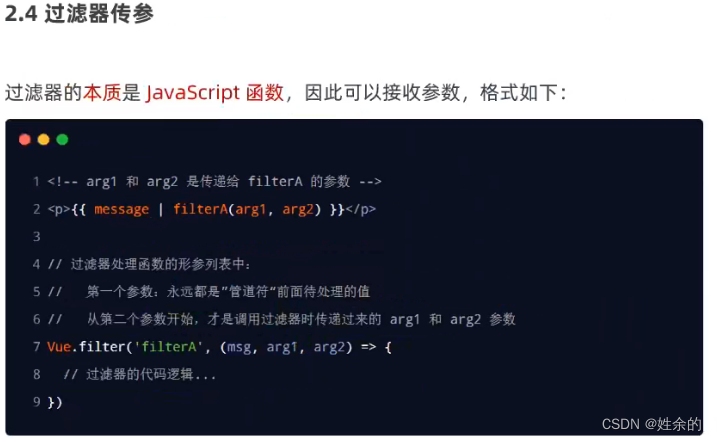
3.2)、过滤器的传参
4)、侦听器
4.1)、方法格式的侦听器
4.2)、对象格式的侦听器
5)、计算属性
5.1)、特点:
1、顶i的时候,要被定义为“方法“
2、在使用计算属性的时候,当普通的属性使用即可
5.2)、好处:
1、实现了代码的复用
2、只要计算属性中依赖的数据源变化了,则计算属性会自动重新求值
例子:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, user-scalable=0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Document</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="./lib/bootstrap.css" />
<style>
.box{
height: 300px;
width: 300px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- 希望vue能够控制下面这个div,帮我们把数据填充到div内部-->
<div id="app">
<span>R</span><input type="text" v-model="r"><br>
<span>G</span><input type="text" v-model="g"><br>
<span>B</span><input type="text" v-model="b"><br>
<hr>
<!-- 专门用户呈现颜色的div盒子-->
<!-- 在属性身上,:达标v-bind :属性绑定-->
<!-- :style 代表动态绑定一个样式对象,他的值是一个 { }样式对象-->
<!-- 当前的样式对象中,只包含了backgroundColor 背景颜色-->
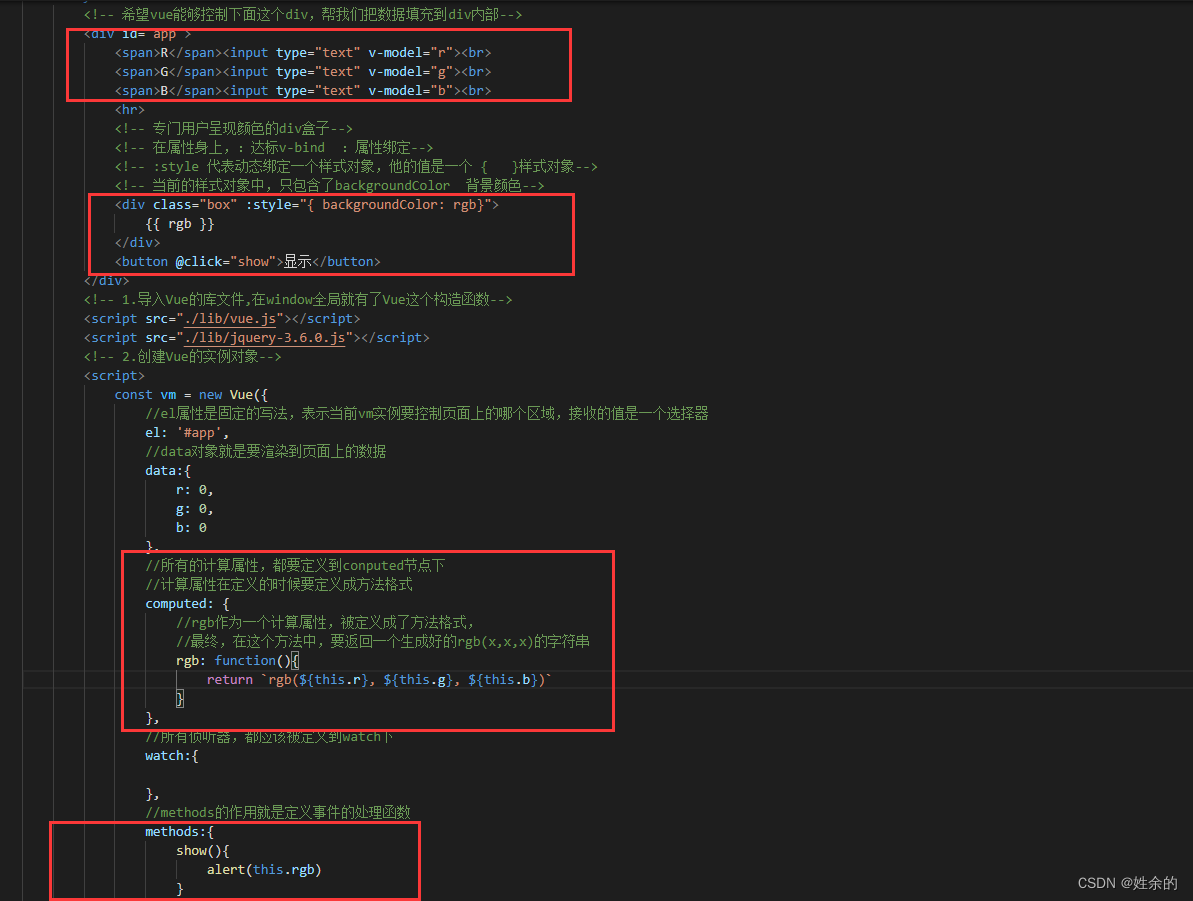
<div class="box" :style="{ backgroundColor: rgb}">
{{ rgb }}
</div>
<button @click="show">显示</button>
</div>
<!-- 1.导入Vue的库文件,在window全局就有了Vue这个构造函数-->
<script src="./lib/vue.js"></script>
<script src="./lib/jquery-3.6.0.js"></script>
<!-- 2.创建Vue的实例对象-->
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
//el属性是固定的写法,表示当前vm实例要控制页面上的哪个区域,接收的值是一个选择器
el: '#app',
//data对象就是要渲染到页面上的数据
data:{
r: 0,
g: 0,
b: 0
},
//所有的计算属性,都要定义到conputed节点下
//计算属性在定义的时候要定义成方法格式
computed: {
//rgb作为一个计算属性,被定义成了方法格式,
//最终,在这个方法中,要返回一个生成好的rgb(x,x,x)的字符串
rgb: function(){
return `rgb(${this.r}, ${this.g}, ${this.b})`
}
},
//所有侦听器,都应该被定义到watch下
watch:{
},
//methods的作用就是定义事件的处理函数
methods:{
show(){
alert(this.rgb)
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
6)、axois
<script>
document.querySelector("#btnGET").addEventListener('click', async function(){
/* axios.get('url'地址,{
//GET 参数
params: {}
})
*/
const { data : res} = await axios.get('http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/getbooks', {
params: {id:1}
})
console.log(res);
})
document.querySelector("#btnPOST").addEventListener('click', async function(){
/* axios.post('url'地址,{
post请求体数据
})
*/
const { data : res} =
await axios.post('http://www.liulongbin.top:3006/api/post',
{
name:'zs', gender:'女'
})
console.log(res);
})
</script>
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_53547097/article/details/125561193
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_39168.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!