Linux shell脚本的调试方法比较多,上次我们探讨和测试了shell内建命令set所提供的一些调试选项,其实 shell 本身也提供了一些调试选项。我们以bash为例来看看。
1 bash 的命令行帮助信息(bash —help)
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ bash —help
GNU bash, version 4.2.46(2)-release-(x86_64-redhat–linux–gnu)
Usage: bash [GNU long option] [option] …
bash [GNU long option] [option] script–file …
GNU long options:
—debug
—debugger
—dump–po-strings
—dump–strings
—help
—init–file
—login
—noediting
—noprofile
—norc
–posix
—protected
—rcfile
—rpm–requires
—restricted
—verbose
—version
Shell options:
–irsD or –c command or -O shopt_option (invocation only)
–abefhkmnptuvxBCHP or -o option
Type `bash –c “help set“‘ for more information about shell options.
Type `bash –c help’ for more information about shell builtin commands.
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $
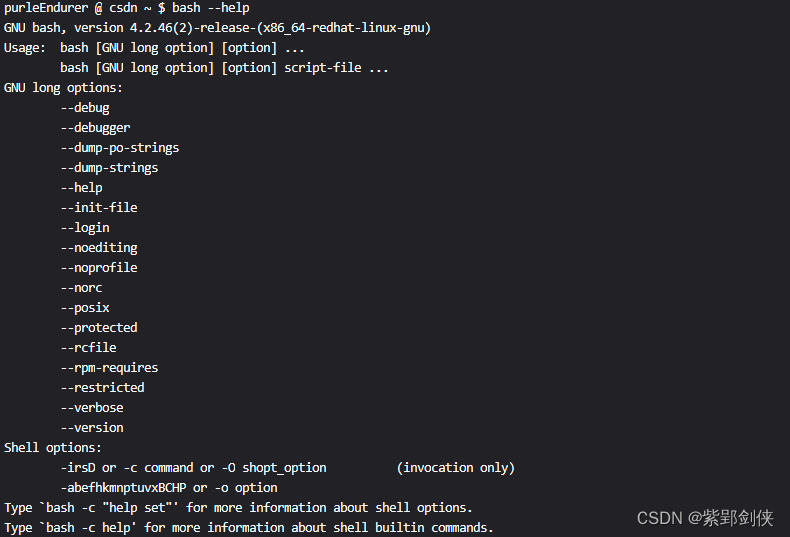
使用 bash 命令加上特定的选项可以在运行Shell脚本时改变其行为,帮助我们诊断问题。
2 bash 的内置命令set提供的选项(bash –c “help set” )
我们可以使用命令 bash –c “help set” 查看 bash 内置命令set提供的选项。
purpleEndurer @ cdu ~ $ bash –c “help set“
set: set [-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option–name] [–] [arg …]
Set or unset values of shell options and positional parameters.
Change the value of shell attributes and positional parameters, or
display the names and values of shell variables.
Options:
-a Mark variables which are modified or created for export.
-b Notify of job termination immediately.
-e Exit immediately if a command exits with a non–zero status.
-f Disable file name generation (globbing).
-h Remember the location of commands as they are looked up.
-k All assignment arguments are placed in the environment for a
command, not just those that precede the command name.
-m Job control is enabled.
-n Read commands but do not execute them.
-o option–name
Set the variable corresponding to option-name:
allexport same as -a
braceexpand same as -B
emacs use an emacs-style line editing interface
errexit same as -e
errtrace same as -E
functrace same as -T
hashall same as -h
histexpand same as -H
history enable command history
ignoreeof the shell will not exit upon reading EOF
interactive-comments
allow comments to appear in interactive commands
keyword same as -k
monitor same as -m
noclobber same as -C
noexec same as -n
noglob same as -f
nolog currently accepted but ignored
notify same as -b
nounset same as -u
onecmd same as -t
physical same as -P
pipefail the return value of a pipeline is the status of
the last command to exit with a non–zero status,
or zero if no command exited with a non–zero status
posix change the behavior of bash where the default
operation differs from the Posix standard to
match the standard
privileged same as -p
verbose same as -v
vi use a vi–style line editing interface
xtrace same as -x
-p Turned on whenever the real and effective user ids do not match.
Disables processing of the $ENV file and importing of shell
functions. Turning this option off causes the effective uid and
gid to be set to the real uid and gid.
-t Exit after reading and executing one command.
-u Treat unset variables as an error when substituting.
-v Print shell input lines as they are read.
-x Print commands and their arguments as they are executed.
-B the shell will perform brace expansion
-C If set, disallow existing regular files to be overwritten
by redirection of output.
-E If set, the ERR trap is inherited by shell functions.
-H Enable ! style history substitution. This flag is on
by default when the shell is interactive.
-P If set, do not follow symbolic links when executing commands
such as cd which change the current directory.
-T If set, the DEBUG trap is inherited by shell functions.
— Assign any remaining arguments to the positional parameters.
If there are no remaining arguments, the positional parameters
are unset.
– Assign any remaining arguments to the positional parameters.
The -x and -v options are turned off.
Using + rather than – causes these flags to be turned off. The
flags can also be used upon invocation of the shell. The current
set of flags may be found in $-. The remaining n ARGs are positional
parameters and are assigned, in order, to $1, $2, .. $n. If no
ARGs are given, all shell variables are printed.
Exit Status:
Returns success unless an invalid option is given.
purpleEndurer @ cdu ~ $
这个信息与
Linux shell编程学习笔记28:脚本调试 set命令![]() https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/134506337?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501中set –help命令显示的帮助信息是一致的。
https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/134506337?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501中set –help命令显示的帮助信息是一致的。
purpleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ bash -c help
GNU bash, version 4.2.46(2)-release (x86_64-redhat-linux–gnu)
These shell commands are defined internally. Type `help’ to see this list.
Type `help name‘ to find out more about the function `name‘.
Use `info bash’ to find out more about the shell in general.
Use `man -k’ or `info‘ to find out more about commands not in this list.A star (*) next to a name means that the command is disabled.
job_spec [&] history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or hist>
(( expression )) if COMMANDS; then COMMANDS; [ elif C>
. filename [arguments] jobs [-lnprs] [jobspec …] or jobs >
: kill [-s sigspec | -n signum | -sigs>
[ arg… ] let arg [arg …]
[[ expression ]] local [option] name[=value] …
alias [-p] [name[=value] … ] logout [n]
bg [job_spec …] mapfile [-n count] [-O origin] [-s c>
bind [-lpvsPVS] [-m keymap] [-f filen> popd [-n] [+N | -N]
break [n] printf [-v var] format [arguments]
builtin [shell-builtin [arg …]] pushd [-n] [+N | -N | dir]
caller [expr] pwd [-LP]
case WORD in [PATTERN [| PATTERN]…)> read [-ers] [-a array] [-d delim] [->
cd [-L|[-P [-e]]] [dir] readarray [-n count] [-O origin] [-s>
command [-pVv] command [arg …] readonly [-aAf] [name[=value] …] o>
compgen [-abcdefgjksuv] [-o option] > return [n]
complete [-abcdefgjksuv] [-pr] [-DE] > select NAME [in WORDS … ;] do COMM>
compopt [-o|+o option] [-DE] [name ..> set [-abefhkmnptuvxBCHP] [-o option->
continue [n] shift [n]
coproc [NAME] command [redirections] shopt [-pqsu] [-o] [optname …]
declare [-aAfFgilrtux] [-p] [name[=va> source filename [arguments]
dirs [-clpv] [+N] [-N] suspend [-f]
disown [-h] [-ar] [jobspec …] test [expr]
echo [-neE] [arg …] time [-p] pipeline
enable [-a] [-dnps] [-f filename] [na> times
eval [arg …] trap [-lp] [[arg] signal_spec …]
exec [-cl] [-a name] [command [argume> true
exit [n] type [-afptP] name [name …]
export [-fn] [name[=value] …] or ex> typeset [-aAfFgilrtux] [-p] name[=va>
false ulimit [-SHacdefilmnpqrstuvx] [limit>
fc [-e ename] [-lnr] [first] [last] o> umask [-p] [-S] [mode]
fg [job_spec] unalias [-a] name [name …]
for NAME [in WORDS … ] ; do COMMAND> unset [-f] [-v] [name …]
for (( exp1; exp2; exp3 )); do COMMAN> until COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
function name { COMMANDS ; } or name > variables – Names and meanings of so>
getopts optstring name [arg] wait [id]
hash [-lr] [-p pathname] [-dt] [name > while COMMANDS; do COMMANDS; done
help [-dms] [pattern …] { COMMANDS ; }
purpleEndurer @ csdn ~ $
2 bash 命令行常用调试选项说明和演示
下面我们就bash命令行中的一些常用的调试选项逐一进行说明和演示。
2.1 echo $-:显示当前已启动的选项
purpleEndurer @ cdu ~ $ echo $-
himBHpurpleEndurer @ cdu ~ $
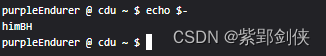
可以看到,当前启用的选项有h、i、m、B和H这几个选项处于启动状态。
2.2 bash -n 脚本文件名说明符:不执行脚本,仅检查错误
-n 选项的功能是:读一遍脚本中的命令但不执行,用于检查脚本中的语法等错误。
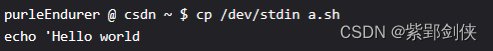
2.2.1 创建测试脚本文件a.sh
我们用 cp 命令来创建 ,文件内容是: echo ‘Hello world
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.sh
echo ‘Hello world
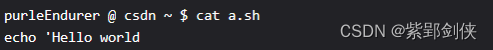
2.2.2 查看测试脚本文件a.sh内容
2.2.3 检查脚本语法错误
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ bash -n a.sh
a.sh: line 1: unexpected EOF while looking for matching `”
a.sh: line 2: syntax error: unexpected end of file
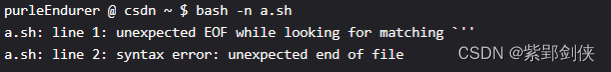
第1个错误出现在第1行:寻找匹配的 ”’ 时出现意外的 EOF,即单引号未配对。
2.3 bash -x 脚本文件说明符:先显示命令及参数(不显示注释),再显示执行结果
bash命令的-x选项与set 命令中的-x选项功能相同,都是打开echo模式,执行命令后,会先显示该命令及所带的参数,再显示命令执行的结果:
2.3.1 创建测试脚本文件a.sh
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ cp /dev/stdin a.sh
echo -n Enter your name please: # 提示用户输入名字
read n # 将用户输入的名字保存到变量n
echo Your name is $n # 显示用户输入的名字 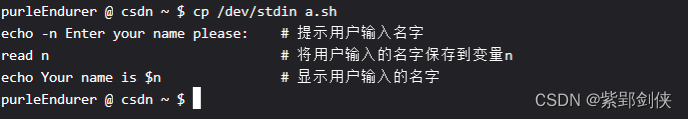
2.3.2 执行脚本文件a.sh
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $ bash -x a.sh
+ echo -n Enter your name please:
Enter your name please:+ read n
purpleEndurer
+ echo Your name is purpleEndurer
Your name is purpleEndurer
purleEndurer @ csdn ~ $

bash会将以+开头,将执行的命令显示出来,然后再显示命令执行的结果。
2.3.3 使用环境变量PS4定制显示格式
其实我们在使用bash的 -x选项来显示命令和参数时前面加的 + 是环境变量PS4 保存的。

因此,我们可以通过修改环境变量PS4的值来设置 bash的 -x选项显示命令和参数时的格式。
例如:我们对显示的命令和参数以 > 开头,然后引入${BASH_SOURCE} 显示脚本文件名,${LINENO}显示行号,${FUNCNAME[0]}显示正在执行的函数的名字:
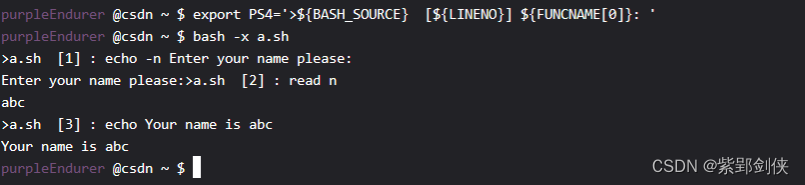
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ PS1=”e[35mpurpleEndurere[0m @csdn w $ “
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ export PS4=’>${BASH_SOURCE} [${LINENO}] ${FUNCNAME[0]}: ‘
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ bash -x a.sh
>a.sh [1] : echo -n Enter your name please:
Enter your name please:>a.sh [2] : read n
abc
>a.sh [3] : echo Your name is abc
Your name is abc
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $
如果觉得字符太多,不容易辨别的话,我们还可以分别给它们加上颜色:
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ export PS4=’e[35m>${BASH_SOURCE} e[0m e[33m [${LINENO}]e[0m e[31m ${FUNCNAME[0]}: e[0m’
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ bash -x a.sh
>a.sh [1] : echo -n Enter your name please:
Enter your name please:>a.sh [2] : read n
abc
>a.sh [3] : echo Your name is abc
Your name is abc
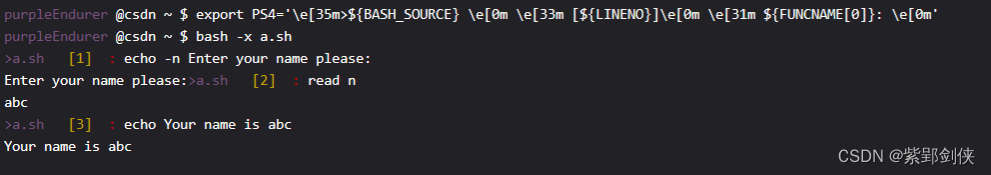
Linux shell编程学习笔记4:修改命令行提示符格式(内容和颜色)![]() https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/133416124?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501中介绍的知识,让脚本文件名以紫色显示,行号以黄色显示,正在执行的函数的名字以红色显示。
https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/133416124?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501中介绍的知识,让脚本文件名以紫色显示,行号以黄色显示,正在执行的函数的名字以红色显示。
2.4 bash -v 脚本文件说明符:一边执行脚本,一边将执行过的脚本命令打印到标准输出(包括注释)
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ export PS4=’e[35m>${BASH_SOURCE} e[0m e[33m [${LINENO}]e[0m e[31m ${FUNCNAME[0]}: e[0m’
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $ bash -v a.sh
echo -n Enter your name please: # 提示用户输入名字
Enter your name please:read n # 将用户输入的名字保存到变量n
abc
echo Your name is $n # 显示用户输入的名字
Your name is abc
purpleEndurer @csdn ~ $

可以看到,-v选项显示所执行的命令不受环境变量PS4的影响,而且会连脚本文件中的注释一并显示。
原文地址:https://blog.csdn.net/Purpleendurer/article/details/134574518
本文来自互联网用户投稿,该文观点仅代表作者本人,不代表本站立场。本站仅提供信息存储空间服务,不拥有所有权,不承担相关法律责任。
如若转载,请注明出处:http://www.7code.cn/show_16365.html
如若内容造成侵权/违法违规/事实不符,请联系代码007邮箱:suwngjj01@126.com进行投诉反馈,一经查实,立即删除!


![[职场] C++开发工程师的岗位职责 #学习方法#笔记](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/dc32c7a3f3c1b6f79ad738d39712c70f.png)
